Thursday, March 29, 2012
Tibetan man set on fire to Protest Chinese President visit to India for the BRICS summit

Wednesday, March 28, 2012
Full disclosure of facebook bugbusters app security vulnerabilities by SANTHOSH TUPPAD
A bit of overview about BugBusters
BugBusters is a facebook app launched by uTest which is a crowd-sourcing community for software testing. This game is a flash game and to look at the game or play the game please visit http://apps.facebook.com/bugsbusters/?ref=ts
This game was launched as a contest which had 3 prizes being first prize as iPad and other 2 prizes as Digital Cameras.
What happened after I discovered the security vulnerabilities?
This game was already live and I could see lot of activity from the users around the globe. Once I found this, I quickly documented the report with the necessary details which could help uTest or the development vendor to fix it.
Once the report was ready, I contacted VP of Marketing Mr. Matt Johnston and Mr. Peter Shih who is a community manager via e-mail. They responded quickly with interest to look into the details. Thanks to Matt for introducing the development company to whom I reported these bugs (The development company name is: Blonde20 – http://blonde20.com/).
Those security vulnerabilities were fixed within the same week I reported them. Thanks to Blonde20 folks for fixing it very soon. The fix was not including the details like Score, Profile ID, profile Name etc. in the POST_DATA form. Once they fixed it I tried reproducing it and could not reproduce the same however, I did not explore for more vulnerabilities for the new fix if there were any because I got busy for the BugDeBug conference and other tasks.
This is all good but, where is full disclosure? Well, I have it for you here.
I did not win the game but, at least for me I am the top most winner and have a feeling of winning billion dollars. I wish all the security testers, researchers, newbie (ethical) hackers to learn from my findings and help the web community to protect from the bad guys out there.
How to Scan & Analyze SSL VPN Server Configuration : SSLyze v0.4 Released
SSLyze is a Fast and Full-Featured SSL Scanner – it enables Better, faster scanning to analyze the configuration of SSL servers.
Supports cipher suites scanning, insecure renegotiation verification, session resumption testing, client certificates, and more. Tested on Python 2.6 & 2.7 with Ubuntu and Windows 7, both 32 and 64 bits. Might work on other platforms as well. Based on OpenSSL and a custom SSL Python wrapper.
We first mentioned SSLyze when it popped up last year in December -
sslyze – Fast and Full-Featured SSL Configuration Scanner
New in v0.4
- Support for OpenSSL 1.0.1 and TLS 1.1 and 1.2 scanning. See –tlsv1_1 and –tlsv1_2.
- Support for HTTP CONNECT proxies. See –https_tunnel.
- Support for StartTLS with SMTP and XMPP. See –starttls.
- Improved/clarified output.
- Various bug fixes.
You can download SSLyze v0.4 here:
Or read more here.
Thursday, March 15, 2012
How LSA Works with/without OSPF AREA 0 | Running OSPF without AREA 0 By Anuj Tyagi: Case Study
Hi Friends, I have received a complete case study done by Mr.Anuj Tyagi on OSPF routing protocol. After reading our article Configure OSPF without AREA 0: CCNP OSPF Case Study, he also tested the similar scenario in his testing LAB. I am publishing his case study as it is without any editing so that guys who are learning networking & OSPF, will get some benefit from this.
Running OSPF without AREA 0
Topology 1: Connecting OSPF Area 2 and area 3 without using ABR.
Interface configurations are mentioned above in the topology.
Remember,
· ABR: ABR is a area border router that contain interfaces in atleast two separate area out of which one should always be in AREA 0.
So, surely above topology don’t have any ABR and we will be going to test how routers behavior in absence of backbone area.
After configuring OSPF routes on R1, R2, R3 as in above topology, we analysis all Routers neighbor table .
That shows Full Neighborship Status for neighbors . Take a look again at the neighbor table,
Neighborship is being maintained with it’s directly connected interfaces.
Now, if we will try to PING
· R2 S0/1 , surely we will get successful reply .
· R2 S0/0, we will get successful reply (as it is directly connected)
· R3 S0/0, obviously we R1 can’t reach 2.2.2.1 of R2 we will be unable to get reply from R3 s0/0.
Why? Just take a look at the neighborship table of R1 again .
So, what is happening behind the scenes when R1 trying to communicate with 2.2.2.0/24 network .
R1 can’t even find the path or from which interface R1 should send the packets .
Now lets take a look at the Router OSPF LSA’s,
· R1 having LSA1 (router-id) updates of only those routers in same area.
Reason : There is no ABR to send LSA3 (summary LSA) updates . ( remember ABR? )
After looking at LSA and neighbor-table, you can guess about the routes will be there in Routing Table.
Again, they are also from directly connected interfaces with Routers.
Now make it a bit interesting, we will going to add interfaces on R2 in Area 0 .
Now, compare neighborship table of Router R1,R2,R2 with and without AREA 0 (backbone area) .
R1 topology table with AREA 0
We can now clearly see LSA3 in the table, apart from networks of Area 0 R1 got one more network advertisement in LSA for 192.168.2.0/24 and 2.2.2.0/24 in summary LSA updates from R2(ABR router).
While in
R2 topology table without AREA 0
In the same way, AREA 0 will also make Router R2 as ABR now and that will add a lot to topology table of Router R2 .
Now, it is behaving like ABR as it is acting as both in AREA-2 and AREA-3 completely.
Router R3 also getting LSA1 and LSA3 updates from R2(ABR).
Note: LSA2 updates (network LSA) are only advertised in Non-broadcast where DR & BDR exist.
Now , also PING will be successful from any Router to any network in topology.
Conclusion:
OSPF will not form neighborship with inter-area(IA) routes if there is no backbone area exist or we do not use ABR . In other words, Each area share it’s link state database only through AREA0 to any other AREA. It will make neighborship only with directly connected networks
LSA 1,2 do not need Area0 to share it’s Acknowledgement but LSA2 will form only in non-broacast network (like frame-relay) where DR will be having responsibility to send updates but we must need to have AREA0 to send LSA 3, 4, 5 & 7 updates.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
R1 Config
Using 1024 out of 57336 bytes
!
version 12.4
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
no service password-encryption
!
hostname R1
!
boot-start-marker
boot-end-marker
!
!
no aaa new-model
memory-size iomem 5
ip cef
!
!
ip auth-proxy max-nodata-conns 3
ip admission max-nodata-conns 3
!
multilink bundle-name authenticated
!
!
archive
log config
hidekeys
!
!
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface Serial0/0
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
clock rate 2000000
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
no ip address
shutdown
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface Serial0/1
no ip address
shutdown
clock rate 2000000
!
router ospf 100
router-id 1.1.1.1
log-adjacency-changes
network 1.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 2
network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 2
!
ip forward-protocol nd
!
!
ip http server
no ip http secure-server
!
!
line con 0
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
!
!
end
-------------------------------------------------------------
R2-ABR Config
R2-ABR#show configuration
Using 1114 out of 57336 bytes
!
version 12.4
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
no service password-encryption
!
hostname R2
!
boot-start-marker
boot-end-marker
!
!
no aaa new-model
memory-size iomem 5
ip cef
!
ip auth-proxy max-nodata-conns 3
ip admission max-nodata-conns 3
!
multilink bundle-name authenticated
!
!
archive
log config
hidekeys
!
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.0.0
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface Serial0/0
ip address 1.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
clock rate 2000000
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
ip address 172.17.1.1 255.255.0.0
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface Serial0/1
ip address 2.2.2.1 255.255.255.0
clock rate 2000000
!
router ospf 100
router-id 2.2.2.2
log-adjacency-changes
network 1.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 2
network 2.2.2.0 0.0.0.255 area 3
network 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 0
network 172.17.0.0 0.0.255.255 area 0
!
ip forward-protocol nd
!
!
ip http server
no ip http secure-server
!
!
control-plane
!
!
line con 0
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
!
!
end
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
R3 Config
Using 1024 out of 57336 bytes
!
version 12.4
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
no service password-encryption
!
hostname R3
!
boot-start-marker
boot-end-marker
!
!
no aaa new-model
memory-size iomem 5
ip cef
!
!
ip auth-proxy max-nodata-conns 3
ip admission max-nodata-conns 3
!
multilink bundle-name authenticated
!
!
!
!
archive
log config
hidekeys
!
!
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface Serial0/0
ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.0
clock rate 2000000
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
no ip address
shutdown
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface Serial0/1
no ip address
shutdown
clock rate 2000000
!
router ospf 100
router-id 3.3.3.3
log-adjacency-changes
network 2.2.2.0 0.0.0.255 area 3
network 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 area 3
!
ip forward-protocol nd
!
!
ip http server
no ip http secure-server
!
control-plane
!
!
!
line con 0
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
!
!
end
Wednesday, March 14, 2012
What is CEF- Cisco Express Forwarding: Load-Balancing with Static Routing
What is CEF- Cisco Express Forwarding: Load-Balancing with Static Routing
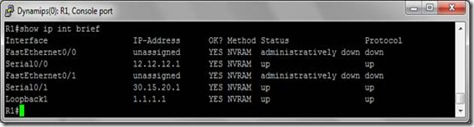
The topology is given below we will be using here :
We made loopbacks each on R1& R2 and configure default static-routing with next hop interfaces on R2.
Configuration is like this :
On R1:
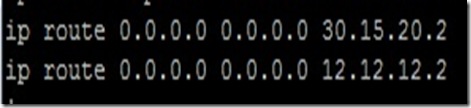
Configuring Default-routes on R1:
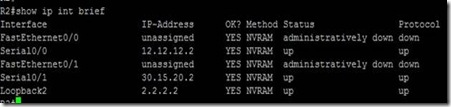
On R2:
Now we did trace route from R1 to Loopback 2.2.2.2 on R2 :
Take a look … it is sending one packet from 12.12.12.0/24 network and other from
And this is what R1 shows but what’s happening behind the scenes on R2 ?
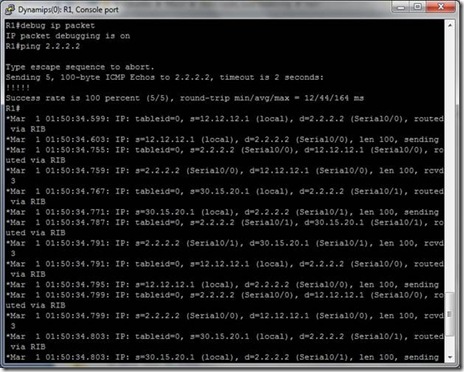
Enabling Debug ip packet on R2 will help to know the sources of packets.
So, this is interesting ….
It shows,
For one packet source is 12.12.12.1 (interface S0/0)
And for another 30.15.20.1 (interface S0/1) and the process take place like this and packets has been sent from each serial interface of R1 alternatively.
But here’s the catch ….
With trace route load-balancing is working fine but when I tried with PING to 2.2.2.2
And as usual #debug ip packets was enabled on R2 . Things are not in favor now L
They are only using same route to send and receive packets.
And at the same time on R1
Note: Routed packets via FIB …
I saw it is following only 30.15.20.0/24 network to send packets. No load balancing.
Look at the above picture carefully,
When R1 is sending packet s=30.15.20.1 , d=2.2.2.2, routed through RIB.
And When R2 is sending Acknowledgement reply for this packet when s=2.2.2.2 and d=30.15.20.1, routed via FIB.
Mummble …. Now whats that CEF, FIB, RIB ??
RIB - routing information base
FIB - forwarding information base
CEF- Cisco Express Forwarding
Once CEF is enabled, it will form the FIB table with the help of Routing table. Now router no longer looks on RIB and FIB acts as replacement for RIB.
CEF also generates adjacency table which pre-maps all of the next hop ip as well as MAC address so as we configure Static routing, CEF add routes to FIB (forwarding information base) and send the packets through the interface which is added first into the table and the static route we have configured first will be added first and will be used to send packets .
Since, here 30.15.20.0/24 is stored first as well as configured first for static route so it will be using 30.15.20.0/24
At the same moment and it will not check the routing table when sending packets to another router/network from then on unless there is change in the routing table and will forward all the packets based on CEF table only.
CEF is ON by default on the routers.
Now, try to debug after Disabling CEF on R1
We are successful to load-balance equally from R1-R2 by disabling CEF. J
NOTE: Routed via RIB not FIB i.e. No longer using FIB table created by CEF.
Now, why?? Why ?? traceroute is able to do load-balancing without disabling CEF ?
Better to find out through practical approach
CEF is enable (by default)
Enable #debug ip packet and
Traceroute to 2.2.2.2
Note : sending broad/multicast .
Now, why it was choosing 30.15.20.0/24 not 12.12.12.10/24 network when we are sending packets through PING??
Hope this is informative for you .
Thank you for reading.
How Routing will be done in between RIPv1 & RIPv2 Routing Protocols
Interoperating RIPV1 & RIPV2 by Anuj Tyagi
Topology is shown below:
R1 - RIP V1 protocol
R2 - RIP V2 protocol
R3 – S0/0 in RIP v1 and S0/1 in RIP v2.
Now, After configuring R3 s0/0 in version 1 and S0/1 in version 2 .
Guess !! What should router show in
#show running-config
Where is RIP version 1 gone ???
There are two important things to look :
- As you enable Rip version 2 on router, it will add version 1 networks to version2 and Rip version1 will get disabled. Reason ? We can’t Run both version RIP version 1 & 2 on same router i.e. If we would like to use version 1 on router for any interface to make neighborship , version 2 should be disabled .
- Routers summarize it’s network routes to it’s Classful boundary. Eg. From above router RIP configuration, we are assigning 2.2.2.0/24 & 1.1.1.0/24 networks but Router summarizing them and send them as 2.0.0.0/8 & 1.0.0.0/8 .
Now, Looking at Routing-table of Routers.
For R1: As router R1 sending routes through RIP version1, it will not make neighborship or receive any updates by default.
For R2& R3:
R3 (version2) not getting updates from R1(version1) for 192.168.1.0 network.
Reason is that simple,
By default, RIP v1 & v2 can interoperate when :
- RIPv1 routers will sent only version1 packets .
- RIPv1 routers will receive both version1 and version2 updates.
- RIPv2 routers will send and receive only version2 updates.
Look at the below routing table of Router R2(version2). It’s getting 1.0.0.0/8 network updates .
So, it’s common to get successful PING from R2 to 1.1.1.2/8.
Reason ?
- 1.1.1.2/8 network is routed through Router RIP version 2. But even if R2 routing table shows 1.0.0.0/8 network in it’s routing table still it will not be able to get any PING REPLY from 1.1.1.2/8.
And if we try to PING from Router R1.
Getting successful PING REPLY from 1.1.1.2/8 is obvious as it is connected directly and doesn’t need any routing updates while R1 can’t able to reach 2.2.2.1/8 as it is not getting VERSION2 updates.
As we know, 1.1.1.1/8 is part of Router R1 which is using Rip version 1.
So, in order to make communication successful we need to make some additional configurations.
Now, question might come in some inquisitive minds why not to just configure RIP v2 on R1. That’s simple but here we want to make communication of RIP v1 with RIPv2.
So, in order to share R1 and R3 to share their routing tables
Either we can use
# ip rip send version2 on s0/0 interface of R1
to send R1 routing updates as version2 but this will not change version of RIP on router R1.
Or
We can configure Router R3 on int s0/0 to be able to receive RIP version1 updates from Router R1.
Now, behind the scenes magic will happen .
Just look at the Routing Table of Router R3 now :
Now, R3 and sharing their updates .
Try to ping f0/0 interface from R3, successful reply.
Now try to ping R3, R2 from R1 :
But we have not used # ip rip receive version 1 on R2 still it is getting updates from Router R3 without using # ip rip send version 1 on int s0/1 of R3.
Conclusion :
- We can’t configure both RIP version 1 &2 on a router at same time. By default, it will run version 1 but when we enable version2, version 1 will get disable automatically.
- By default, RIP version 1 will send only version 1 updates but can send both version 1&2 updates, But RIP version 2 will only send and receive version 2 updates.
- To enable RIP version 1 to send version 2 updates , we need to configure
(config-int)#ip rip send version 2
on interface .
- To enable RIP version 2 to receive both version 1&2 updates . we configure:
(config-int)#ip rip receive version 1 2
- Considering the same topology in this document, as we config #ip rip send/receive on R1& R3 interface, R2 will get R1(version 1)updates from R3 without configuring any special configuration (#ip rip send/receive version x) except Router RIP on R3 s0/1 and R2 s0/0.
Tuesday, March 13, 2012
ESET NOD32 KEYS | Latest updates | FRESH username | ESET Nod32 Username And Password [03/13/2012]
Username:TRIAL-62489867
Password:rr4h33b88b
Username:TRIAL-62489874
Password:tjunjrdxec
Username:TRIAL-62489876
Password:muurpv48dh
Username:TRIAL-62489885
Password:xb8ka36j5p
Username:TRIAL-62489892
Password:352rsp78br
Username:TRIAL-62489900
Password:prjrbmarrd
Username:TRIAL-62489910
Password:8p6t3p3j76
Username:TRIAL-62489922
Password:m53esdsrem
Username:TRIAL-62489933
Password:bkttme84j2
Username:TRIAL-62489945
Password:57xkcv2fhv
Username:TRIAL-62489957
Password:dfhs86ekvu
Username:TRIAL-62489964
Password:xkuhm5tknu
Username:TRIAL-62489974
Password:ejemb7kd5n
Username:TRIAL-62489987
Password:72ssdspkpb
How to configure Static VRRP over Cisco router
Hi all,
I was working over 7200 routers for HSRP and VRRP implementation, and thought why not to cover an article over it. I will be covering Static VRRP over Cisco routers in GNS3 and will be showing you how to test it. you can also read my basic GNS3 tutorial over Cisco routers if you wish
GNS 3 Tutorial – Basic Router password Configuration
A bit about VRRP from Cisco Documentation.
The Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) is an election protocol that dynamically assigns responsibility for one or more virtual routers to the VRRP routers on a LAN, allowing several routers on a multiaccess link to utilize the same virtual IP address. A VRRP router is configured to run the VRRP protocol in conjunction with one or more other routers attached to a LAN. In a VRRP configuration, one router is elected as the virtual router master, with the other routers acting as backups in case the virtual router master fails.In layman's terms, it allows for switching of routers in case a link fails or flaps. I have left some advanced parts from this tutorial, this is completely for those who have a general idea of Cisco CLI and want to learn how to configure fault tolerant VRRP over cisco routers.
Here is the GNS3 topology I will be using for this tutorial
Now, fire up your GNS3 and start by configuring all the routers. Click on the console button over titlebar to start putty terminal.the first step is to configure telnet over routers R3.
(PS: I have kept the passwords simple for the sake of simplicity, don't try this habit in an actual scenario.)
Router R3
Router>enOnce done, Lets configure the R3 router and assign IP address over it.
Router#conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#line vty 0
Router(config-line)#password r3
Router(config-line)#login
Router(config-line)#exit
Router(config)#int s0/0
Router(config-if)#ip add
Router(config-if)#ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.252
Router(config-if)#no sh
Router(config)#int s0/1
Router(config-if)#ip address 2.1.1.1 255.255.255.252
Router(config-if)#no sh
Router(config-if)#
Router(config-if)#exit
Router(config)#
So far, router R3 has been configured. Do the same for all others. make sure to assign R4 and R5 same lan IP.
Router R4
Router>enand Interface IP's
Router#conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#line vty 0
Router(config-line)#password r4
Router(config-line)#login
Router(config-line)#exit
Router(config)#int s0/0Router R5
Router(config-if)#ip add
Router(config-if)#ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.252
Router(config-if)#no sh
Router(config)#int e1/0
Router(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#no sh
Router(config-if)#
Router(config-if)#exit
Router(config)#
Router>enand Interface IP's
Router#conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#line vty 0
Router(config-line)#password r5
Router(config-line)#login
Router(config-line)#exit
Router(config)#int s0/0Once done, its time to add some routes to the routers. After doing it, Ping everything to every lan/wan just to be safe and sure.
Router(config-if)#ip add
Router(config-if)#ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.252
Router(config-if)#no sh
Router(config)#int e1/0
Router(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#no sh
Router(config-if)#
Router(config-if)#exit
Router(config)#
Router R3
Router(config)#ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 1.1.1.2
Router(config)#ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 2.1.1.2 20
Router R4
Router(config)#ip route 2.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.2 20
Router(config)#ip route 2.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 1.1.1.1
Router R5
Router(config)#ip route 1.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 2.1.1.1 20
Router(config)#ip route 1.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1
If it doesnt pings, then you might have screwed up some where.
Run "sh ip route" over router to check configuration.
Router 3
Router#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
1.0.0.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 1.1.1.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0
2.0.0.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 2.1.1.0 is directly connected, Serial0/1
S 192.168.1.0/24 [1/0] via 1.1.1.2
Router R4
Router#sh ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
1.0.0.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 1.1.1.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0
2.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
S 2.1.1.0 [1/0] via 192.168.1.2
[1/0] via 1.1.1.1
C 192.168.1.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet1/0
Router R5
Router#sh ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
1.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
S 1.1.1.0 [1/0] via 192.168.1.1
2.0.0.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 2.1.1.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0
C 192.168.1.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet1/0
Till here, basic configuration has been done. now we will configure VRRP over R4 on ethernet interface.
Now in very very simple terms,
- We will be tracking an interface (by giving it a track id) which in case if goes down the router shall switch states, in this case its the serial link from Router R3 to R4 (serial 0/0)
- We will be creating a group of routers (here R4 and R5),
- Assign a group ID to them (which is "1" btw) ,
- After that, we will create a Virtual gateway over both routers which will be always up in case any router goes down (and thats why we gave both routers IP's from same lan) .
- Then will select one of them as Master router and Rackup router (R4 in this case and R5 as Backup) and assign priority to them (higher is important, default is 100, 200 to R4, default to R5).
- We will specify a decreasing value which shall be subtracted from priority which will preempt it to switch to router with higher priority, which in this case is 110. As serial link from R3 to R4 fails, 110 will be subtracted from 200 and hence R5 will have a higher priority 100 > then priority of R4 which is 90, hence it will become the Master router.
- Test it :)
Router R4
Assign track id to Serial interface, which will be monitored by R4 .
Router(config)#track 1 interface serial 0/0 line-protocol
Router(config-track)#exit
Then configuring VRRP over it.
Router(config)#int e1/0
Router(config-if)#vrrp 1 ip 192.168.1.3
Router(config-if)#vrrp 1 priority 200
Router(config-if)#vrrp 1 preempt
Router(config-if)#vrrp 1 track 1 decrement 110
Router(config-if)#exit
Hence the final configuration upon "sh vrrp" will be
Ethernet1/0 - Group 1
State is Master
Virtual IP address is 192.168.1.3
Virtual MAC address is 0000.5e00.0101
Advertisement interval is 1.000 sec
Preemption enabled
Priority is 200
Track object 1 state Up decrement 110
Master Router is 192.168.1.1 (local), priority is 200
Master Advertisement interval is 1.000 sec
Master Down interval is 3.218 sec
Now we need to configure VRRP over Router 5
Router 5
Not much to do here except to enable preempt and VRRP..
Router(config)#int e1/0
Router(config-if)#vrrp 1 ip 192.168.1.3
Router(config-if)#vrrp 1 preempt
Router(config-if)#exit
hence final configuration of Router 5 will be
Ethernet1/0 - Group 1
State is Backup
Virtual IP address is 192.168.1.3
Virtual MAC address is 0000.5e00.0101
Advertisement interval is 1.000 sec
Preemption enabled
Priority is 100
Master Router is 192.168.1.1, priority is 200
Master Advertisement interval is 1.000 sec
Master Down interval is 3.609 sec (expires in 3.201 sec)
Congrats :) you have configured VRRP over your routers. Now to check , if its working or not, first traceroute your packet to 192.168.1.0 lan from Router R3
Router#traceroute 192.168.1.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Tracing the route to 192.168.1.1
1 1.1.1.2 56 msec 88 msec *
Its going through our primary router :) now telnet from Router R3 to virtual gateway.
Router#telnet 192.168.1.3
Trying 192.168.1.3 ... Open
User Access Verification
Password:
Router>
If the password which gives you access is r4, then its configured correctly as of now. Now , lets shut unshut the primary serial interface from Router R3 .
Router#
Router#conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#int s0/0
Router(config-if)#sh
Router(config-if)#exit
Router(config)#
*Mar 1 00:57:27.927: %LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface Serial0/0, changed state to administratively down
*Mar 1 00:57:28.927: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial0/0, changed state to down
Router(config)#exit
Router#
*Mar 1 00:57:38.483: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
Router#
Good, now ping virtual gateway
Router#ping 192.168.1.3
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.1.3, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 20/49/80 ms
its working fine, now traceroute the packet to 192.168.1.0 lan from Router R3
Router#traceroute 192.168.1.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Tracing the route to 192.168.1.1
1 2.1.1.2 64 msec 68 msec 64 msec
2 192.168.1.1 44 msec 68 msec *
:)) its working too..now finally we login into virtual gateway from Router R3 and i assume we will login into Router R5, and then lets check out the VRRP configuration by running "sh vrrp" command.
Router#
Router#telnet 192.168.1.3
Trying 192.168.1.3 ... Open
User Access Verification
Password:
Router>sh vrrp
Ethernet1/0 - Group 1
State is Master
Virtual IP address is 192.168.1.3
Virtual MAC address is 0000.5e00.0101
Advertisement interval is 1.000 sec
Preemption enabled
Priority is 100
Master Router is 192.168.1.2 (local), priority is 100
Master Advertisement interval is 1.000 sec
Master Down interval is 3.609 sec
which works :) as Router R5 is the Master Router for now. Now disconnect from Router R5 and unshut the serial interface from Router R3, login into virtual gateway again and then check out the VRRP configuration by running "sh vrrp" command.
Router#exit
[Connection to 192.168.1.3 closed by foreign host]
Router#conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#int s0/0
Router(config-if)#no sh
Router(config-if)#exit
Router(config)#
*Mar 1 01:08:41.739: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Serial0/0, changed state to up
*Mar 1 01:08:42.743: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial0/0, changed state to upexit
Router#
*Mar 1 01:08:46.955: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
Router#telnet 192.168.1.3
Trying 192.168.1.3 ... Open
User Access Verification
Password:
Router>sh vrrp
Ethernet1/0 - Group 1
State is Master
Virtual IP address is 192.168.1.3
Virtual MAC address is 0000.5e00.0101
Advertisement interval is 1.000 sec
Preemption enabled
Priority is 200
Track object 1 state Up decrement 110
Master Router is 192.168.1.1 (local), priority is 200
Master Advertisement interval is 1.000 sec
Master Down interval is 3.218 sec
Router>
Excellent..VRRP has been fully configured as the Router R4 is again the Master Router :)
Congrats..you have successfully configured the VRRP over Static on Cisco Routers and fully tested it for fault tolerance .
till then
Stay Gold :))
Related Posts
- Best Security Magazine | Top IT Security Magazine and Zines Reviewed | Best Hacking Magazines Listed
- Scroogled – Google Tracks Spies You | Amazing Story by Cory Doctorow
- Top Indian Hackers | Real Hackers of India
- Google Celebrates Pacman – The Best Google Doodle Ever :)
- BSNL router hacking and possibility of running custom code over it

About the author : Rishabh Dangwal
Rishabh Dangwal is a no-nonsense network geek who has got a thing for guitars, retro games and emulators. When he is not tinkering with devices and gadgets, he can be found reading novels by Fredrick Forsyth. Follow him on Twitter
Sunday, March 11, 2012
How OSI 7 Layer Model Works? Understanding OSI Layers
This article aims to study the 7 layers of OSI model used by Computer system, when communicating with any other system in same/ different network.
Note: This article is not about understanding OSI layers. It is a practical approach for how OSI layers works & used by our computer system.

Application Layer: Application Layer provides user interface i.e. user directly interacts with this layer. The most common examples of applications which enable us to communicate through different protocols are :
- FTP (Eg. Filezilla Server Application)
- http/https (Eg. Firefox or any other Web-browser)
- SMTP ( via any email client like IBM LOTUS or Microsoft Outlook or WebBrowser)
- Telnet ( shell interpretaors like Command Prompt in windows/ terminal in linux distro)
Presentation Layer: This layer gets name from it’s purpose . This layer responsibility includes :
- Presents data to application layer and responsible for data translation and formatting. Eg. Translation of data we enter into browser to be converted into web language codes with different tags . Also it takes care of data which has been sent should be understood by browser to present it on user-interface .
- Compression and encryption of data .

I tried to capture a packet for PING REQUEST to www.google.com and on capturing packets got this in packets.
For compression, take an example of browser which uses HTTP Compression to save transfer data volume and speeds ups Web page load time. Firefox uses Gzip encoding to send data .
- We proved that presentation layer also used by & within computer system .

This command is common for windows/Linux OS.
Transport Layer : This layer is concerned with reliability of data transfer .
It is of two types :
- Connection Oriented (TCP)
- Connectionless (UDP)
It also take care of other responsibilities like :
Flow Control (windows) : Which find how much data should be send in one packet during transfer to minimize the data loss due to buffer overflow. It doesn’t send data but Segment into smaller pieces and size of which is defined through windowing feature. To show this in practical manner, I started to upload a file on mediafire.com .

By ping , we got ip address of mediafire.com .it’s 205.196.120.8 .
And Now I started to sniff the packets using wireshark on my pc. So, it’s easy to confirm that below captured packets are those during transfer from mediafire. .

So, what do we learn from above image ?
Source address: 205.196.120.8
Destination address: 192.168.1.3
Protocol type: TCP (connection oriented )
Win (window size ): 66240 bytes = 65 KB approx .
Source address is mediafire server as we are uploading data.
So, what conclusion it makes ? Data is being split up into 66240 bytes each and after reaching destination it being re-ordered.
The segments which are delivered are acknowledged back to the sender upon their reception.
Network Layer: Network layer works on Logical address which is IP addresses. A computer system understand IP addresses and communication and identification also takes place in computer system.

Any device which use ip-address for communication
Data Link Layer : The main focus of data link layer on use of MAC address. Whenever data flows through the LAN , communication takes place through MAC address .
So, to find if MAC address is being used during data transfer in lan or not ?
I start capturing again using wireshark .

Which shows Destination MAC address : 00:26:5e:ff:c5:fc for 192.168.1.3
Source MAC address: 00:26:5e:fc:10:Se for 192.168.1.2 .

Physical Layer :
This layer conveys the bit stream through the network at the electrical and mechanical level. It provides the hardware means of sending and receiving data on a carrier.
The Physical Layer defines electrical and physical specifications for devices. In particular, it defines the relationship between a device and a transmission medium, such as a copper or optical cable.
The major functions and services performed by the Physical Layer are:
- Establishment and termination of a connection to a communications medium.
- Participation in the process whereby the communication resources are effectively shared among multiple users. For example, contention resolution and flow control.
- Modulation, or conversion between the representation of digital data in user equipment and the corresponding signals transmitted over a communications channel.


So, during transfer of data, various instructions and signals executed whichch converted into binary language . Similarly, when we transfer data from our system to any other then transfer takes place through various components and leave through cable.














![clip_image013[1] clip_image013[1]](http://lh3.ggpht.com/--Pl2ctzHHWo/TjAMQp78-yI/AAAAAAAAGQ0/i175IcRTS54/clip_image013%25255B1%25255D_thumb%25255B1%25255D.jpg?imgmax=800)